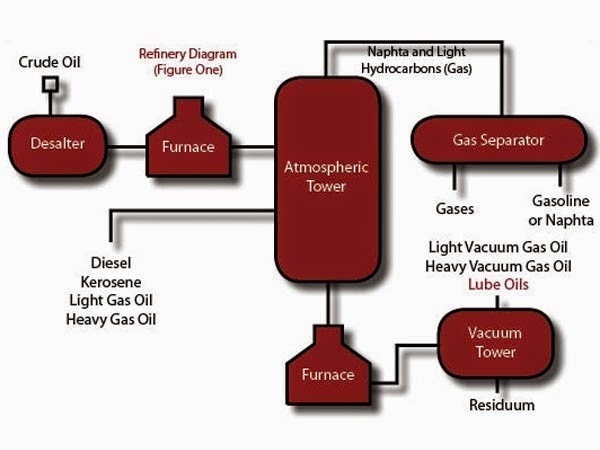
An oil field is a tract of land used for extracting petroleum, otherwise known as crude oil, from the ground. Although some contest the exact origin of oil, most consider petroleum a fossil fuel created from dead organic material often found in ancient seabeds thousands of meters below the surface of the earth.
BREAKING DOWN Oil Field
An oil field consists of a reservoir in the rocky strata of the Earth which traps hydrocarbons. An impermeable or sealing rock layer covers the reservoir. Typically, industry professionals use the term “oil field” with an implied assumption of economic size.
There are more than 65,000 oil fields around the world, many of the largest located in the Middle East. There have been tens of thousands of oil fields have been discovered. However, the concentration of 94-percent of known reserves is in fewer than 1500 major oil fields. The locations of oil fields have been the origin of past geopolitical conflicts and environmental concerns.
Complications of Establishing an Oil Field
Establishing an oil fields in Pakistan can be a herculean feat of logistics. It can include establishing the infrastructure necessary for what can be decades of extraction, production, and maintenance. Oil companies often contain entire divisions that are responsible for infrastructure construction and specialized services which are required to operate a profitable oil field. Oil fields are dotted with a variety of extraction equipment which includes drilling rigs, offshore platforms, pump jacks, and more. There may also be exploratory wells probing the edges, pipelines to transport the oil elsewhere, and support facilities.
In recent years, new technologies in oil exploration and production have dramatically increased the productivity levels of oil fields. These include horizontal drilling, hydraulic drilling, hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, and the use of proppant. Proppant is a mixture of water and sand used to keep the fractured pathways to the wellbore clear.
These technologies, coupled with advances such as seismic technology, helped to increase oil field efficiency rates and contributed to a glut in oil supply, which drove oil prices down. Companies that work oil fields remain focused on technological development to lower their production costs in the current price-pressured environment.